There are now over 21 billion IoT devices online worldwide, according to IoT Analytics’ 2025 tracking data. That’s roughly 2.5 connected devices for every human on Earth. And here’s what caught my attention after 12 years consulting on IoT applications across healthcare, manufacturing, and smart cities: most people still don’t grasp how deeply this technology shapes their Tuesday mornings, their hospital visits, or their commute.
I’ve watched a single temperature sensor save a pharmaceutical company $2.3 million in spoiled inventory. I’ve also seen a poorly secured smart thermostat become the entry point for a ransomware attack that shut down a 200-person office for three days.
Both stories are real. Both happened in 2025. And both tell you something important about where IoT technology stands right now.
In this article, I’ll walk you through what IoT applications actually look like in 2026, the genuine advantages of IoT that go beyond marketing fluff, the disadvantages of IoT that vendors prefer you ignore, and why IoT technology security concerns should keep every connected business up at night. Whether you’re exploring IoT training for a career shift or evaluating connected devices for your organization, you’ll leave with a clearer picture than you had five minutes ago.
Page Contents
What Are IoT Applications?
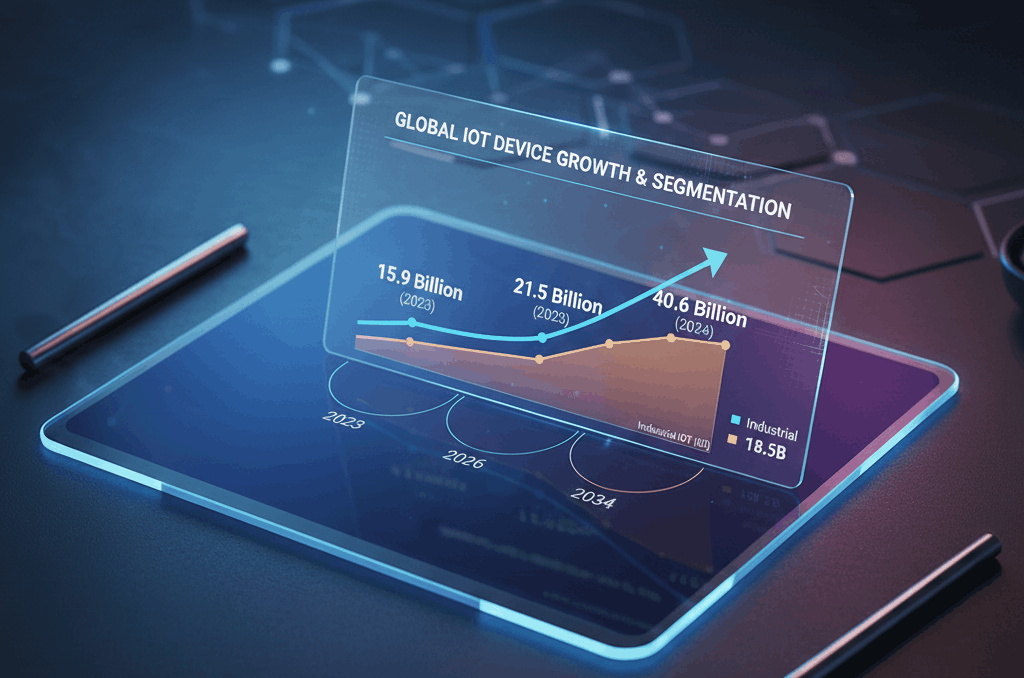
IoT applications are real-world uses of the Internet of Things, a network of physical objects (sensors, machines, wearables, vehicles, appliances) embedded with software and connectivity that allows them to collect and share data without human input. These applications span smart homes, precision agriculture, remote patient monitoring, industrial automation, and city infrastructure. As of early 2026, IoT technology connects an estimated 21.5 billion devices globally, according to Statista, with projections reaching 40.6 billion by 2034.
Why IoT Applications Matter More in 2026 Than Ever Before
The IoT conversation has shifted. Five years ago, it was about possibilities. Now it’s about consequences.
According to Fortune Business Insights, the global IoT market hit $714.48 billion in 2024 and is on track to cross $4.06 trillion by 2032, growing at a 24.3% compound annual rate. That’s not speculation from a startup pitch deck. That’s capital flowing into factories, hospitals, farms, and power grids at a pace that makes IoT impossible to ignore.
But here’s what shifted the conversation for me personally. In mid-2025, working with a logistics client in Bengaluru, I watched their IoT-powered fleet tracking system reduce fuel costs by 18% in 90 days. Not because the technology was new. Because they finally integrated real-time sensor data with their route planning AI. The devices had been installed for two years. Nobody was using the data properly.
That’s the real story of IoT in 2026. The hardware is everywhere. The advantages of IoT only show up when you actually connect the data to decisions.
What’s Changed Since 2023?
Three forces reshaped IoT applications between 2023 and now. First, 5G rollouts accelerated low-latency connections, making real-time industrial IoT practical in areas that previously relied on spotty LTE. IoT Analytics reports the cellular IoT chipset market reached $4.07 billion in 2024 alone, with 5G chipsets projected to hit $9.31 billion by 2030. Second, edge AI integration became standard, so devices now process data locally instead of shipping everything to the cloud. Third (and this one’s uncomfortable), the EU Cyber Resilience Act, with reporting obligations starting September 2026, finally forced manufacturers to take security seriously.
How IoT Technology Works: 7 Applications That Actually Deliver Results
IoT technology follows a four-stage cycle: sensors collect data, connectivity transmits it, platforms process it, and interfaces let humans (or AI) act on it. Simple concept. The execution is where things get interesting.
Here are seven IoT applications producing measurable outcomes right now.
1. Smart Homes
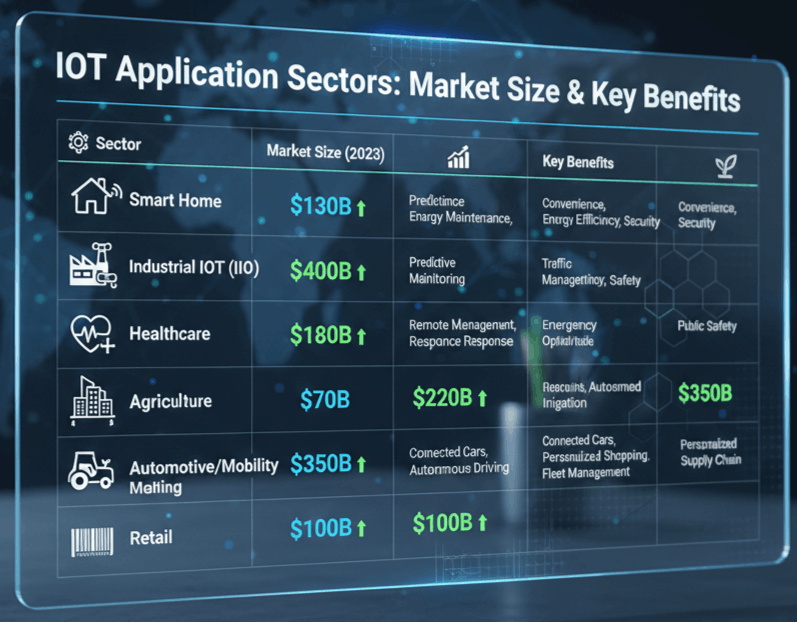
The global smart homes market reached $183.2 billion in 2024, growing at 8.5% annually. The average U.S. household now uses 21 IoT-connected devices, up from 15 just two years ago. We’re not just talking about Alexa playing music. Smart thermostats from companies like Ecobee and Google Nest cut heating costs by 15-23%, while connected security systems from Ring and SimpliSafe let homeowners monitor properties from anywhere.
(I’ll be honest, my own smart home setup has saved me from leaving the garage door open at least a dozen times. Small thing, but it adds up.)
2. Healthcare and Remote Patient Monitoring
This is where IoT applications get genuinely life-changing. The healthcare IoT market is projected to reach $332.67 billion by 2027, per industry estimates. Wearable glucose monitors from Dexcom, remote cardiac devices from Abbott, and smart pill dispensers are helping patients manage chronic conditions without weekly doctor visits. Medical facilities will employ roughly 7.4 million IoT devices by 2026.
But there’s a flip side. Attacks on medical IoT devices jumped 123% year-over-year, and healthcare IoT breaches now average $10 million per incident. More on that in a minute.
3. Industrial IoT (IIoT) and Smart Manufacturing
The Industrial Internet of Things connects factory machines, robotic arms, and environmental sensors to central platforms. Companies like Siemens, Bosch, and GE Digital use IIoT to predict equipment failures before they happen, cutting unplanned downtime by up to 50%. The average cost of an industrial IoT breach reached $5.56 million in 2025, which tells you both how valuable and how targeted these systems are.
4. Smart Cities and Urban Infrastructure
IoT-powered traffic lights and sensors now operate in 145 U.S. cities, reducing congestion by an average of 12%. The IoT smart cities market is predicted to surpass $312 billion by 2026. Municipal spending on connected infrastructure covers everything from waste management to public Wi-Fi to air quality monitoring. Barcelona’s smart water management system, one of the earliest large-scale deployments, has saved the city over $58 million annually in water costs.
5. Precision Agriculture
Soil moisture sensors, GPS-guided tractors from John Deere, and drone-based crop monitoring let farmers optimize water usage and fertilizer application down to the square meter. IoT-driven precision agriculture has been shown to reduce water consumption by 25-30% while increasing yields by 15-20% in pilot programs across India and the American Midwest.
6. Energy Management
Smart meters, connected HVAC systems, and real-time grid monitoring help utilities balance load and reduce waste. The energy sector saw a staggering 459% increase in IoT-based cyberattacks from mid-2024 to mid-2025, which tells you how central these systems have become to critical infrastructure.
7. Supply Chain and Fleet Management
Real-time shipment tracking, cold-chain monitoring for pharmaceuticals, and predictive maintenance for delivery vehicles are now table stakes for competitive logistics. The IoT fleet management market is estimated at $55 billion for 2026. Remote asset monitoring was the top enterprise IoT use case in 2025, with 34% of organizations citing it as their primary application.
Advantages and Disadvantages of IoT: An Honest Breakdown
You’ll find plenty of articles listing pros and cons of IoT in tidy bullet points. I want to give you something more useful: context for when each advantage actually plays out, and which disadvantages are deal-breakers versus manageable trade-offs.
The Real Advantages of IoT
Operational cost reduction is the headliner. According to a Vodafone IoT Barometer report, 54% of enterprises using IoT technology reported measurable cost savings. That’s not hype. A mid-size warehouse deploying smart inventory tracking typically sees 20-30% fewer stockouts and 15% lower labor costs within the first year.
Decision-making speed improves dramatically when you’re working with real-time data instead of weekly reports. A factory floor manager watching vibration sensors on critical machinery can schedule maintenance before a breakdown, not after. That shift from reactive to predictive saves both money and headaches.
Remote monitoring changes what’s possible. A cardiac patient in rural Tamil Nadu can share vital signs with a specialist in Chennai without a six-hour bus ride. A farmer in Iowa can check soil conditions across 500 acres from a phone. These aren’t futuristic promises. They’re happening now.
The Disadvantages of IoT Nobody Wants to Talk About
Security is not just a concern. It’s a crisis. IoT devices face approximately 820,000 attacks daily worldwide as of 2025-2026. One in three data breaches now involves an IoT device, according to Verizon’s Data Breach Investigations Report. And here’s the part that should worry you: IoT breach attempts surged 84% in 2025, primarily through weak device-level security like default passwords and unpatched firmware.
Interoperability is still a mess. Your Philips Hue lights might not talk to your Samsung SmartThings hub the way you’d expect. Enterprise deployments face the same headache at scale. Different protocols (Zigbee, Z-Wave, Matter, MQTT, CoAP) create integration nightmares that add months to project timelines. The Matter standard from the Connectivity Standards Alliance is helping, but adoption is slower than the press releases suggest.
Privacy trade-offs are real. Every IoT device is a data collection point. Your smart speaker records ambient audio. Your fitness tracker knows your sleep patterns, heart rate, and location. More than 25% of IoT-related breaches involve stolen personal data, according to IBM X-Force Threat Intelligence. You’re trading convenience for surveillance, and most people don’t realize the exchange they’ve made.
Over-reliance on connectivity creates fragility. When your internet goes down, your smart lock might lock you out of your own house. (Yes, I’ve had this happen.) When a cloud platform experiences an outage, thousands of “smart” devices become expensive paperweights. This dependency on always-on connectivity is a structural weakness that gets worse as more critical systems go online.
Advantages vs. Disadvantages of IoT at a Glance:
| Advantages of IoT | Disadvantages of IoT |
| 20-30% cost reduction in operations | 820,000 daily cyberattacks on IoT devices |
| Real-time data for faster decisions | Protocol fragmentation (Zigbee, Z-Wave, Matter) |
| Remote monitoring across distances | 25%+ of breaches involve stolen personal data |
| Predictive maintenance prevents downtime | Cloud dependency creates single points of failure |
IoT Technology Security Concerns: The Risks You Can’t Afford to Ignore
Let me be direct. IoT technology security concerns are the single biggest barrier to long-term IoT adoption, and the data backs this up.
In July 2025, Google disclosed BadBox 2.0, the largest known botnet of internet-connected TVs. Over 10 million smart TVs, projectors, and infotainment systems were compromised with pre-installed malware, turning living room devices into tools for click-fraud campaigns and DDoS attacks. Around the same time, a misconfiguration at Mars Hydro, a grow-light manufacturer, exposed 2.7 billion IoT device records, including Wi-Fi credentials and device identifiers.
Those aren’t hypothetical scenarios from a cybersecurity whitepaper. They happened. And they illustrate why 84% of IoT adopters report experiencing at least one breach.
What Can You Actually Do About It?
If you’re deploying or managing IoT devices, here’s what works in practice:
- Change default credentials immediately. One in five IoT devices still uses factory passwords. That’s the digital equivalent of leaving your front door unlocked.
- Segment your network. Keep IoT devices on a separate VLAN from your main business systems. If a smart camera gets compromised, it shouldn’t give attackers a path to your financial data.
- Patch firmware religiously. Unpatched firmware is responsible for 60% of IoT security breaches, according to the IoT Security Foundation.
- Maintain a device inventory. You can’t secure what you don’t know exists. Many breaches trace back to forgotten devices still connected to the network.
- Watch for regulatory changes. The EU Cyber Resilience Act’s reporting obligations begin September 2026. CISA’s CPG 2.0 now unifies IT, IoT, and OT security goals in the U.S. If you’re not prepared, you’ll face compliance penalties on top of breach costs.
Where IoT Training Fits In
Here’s the kicker. The biggest bottleneck for IoT adoption isn’t hardware costs or connectivity. It’s people.
IoT training has become one of the fastest-growing segments in tech education, and for good reason. Organizations need professionals who understand the full stack: sensors and embedded systems, network protocols, cloud platforms like AWS IoT Core and Microsoft Azure IoT Hub, data analytics, and cybersecurity. That combination of skills is rare, which means IoT training programs from platforms like Coursera (offered through institutions like Stanford and the University of Michigan), Cisco’s IoT Fundamentals specialization, and AWS IoT certification tracks can meaningfully accelerate your career.
In my experience, the professionals who thrive in IoT aren’t specialists in one area. They’re people who can connect the dots between a malfunctioning sensor, a data pipeline issue, and a security vulnerability. That cross-disciplinary thinking is what makes IoT training valuable, and what makes the field exciting.
Frequently Asked Questions About IoT Applications
How many IoT devices are connected worldwide in 2026?
Approximately 21.5 billion IoT devices are connected globally as of early 2026, according to Statista and IoT Analytics. That number is expected to reach 25 billion later in 2026 and surpass 40 billion by 2034, driven by 5G expansion, edge AI, and industrial adoption.
What are the biggest advantages of IoT for businesses?
The top advantages of IoT include measurable cost reduction (54% of enterprises report savings), real-time data for faster decisions, predictive maintenance that prevents costly downtime, and remote monitoring capabilities. The most impactful gains come when sensor data is integrated with analytics platforms, not just collected.
What are the main disadvantages of IoT?
Key disadvantages of IoT include security vulnerabilities (820,000 daily attacks), interoperability issues between protocols and platforms, privacy risks from constant data collection, and over-reliance on internet connectivity. For businesses, unpatched firmware and default credentials remain the most common causes of breaches.
Is IoT safe to use at home?
IoT is safe when you follow basic security practices. Change default passwords, keep firmware updated, and use a separate Wi-Fi network for smart devices. Connected homes faced an average of 29 daily attack attempts in 2025, triple the rate from 2024, so don’t skip these steps.
What IoT training should I pursue for a career in connected technology?
Start with foundational certifications from Cisco (IoT Fundamentals) or AWS (IoT Core certification). For deeper knowledge, Coursera offers IoT specializations from Stanford and the University of Michigan. Focus on building cross-disciplinary skills: embedded systems, network protocols, cloud platforms, and cybersecurity.
How much does an IoT security breach cost?
The average IoT security incident costs businesses $330,000, according to NIST. However, costs vary dramatically by sector. Healthcare IoT breaches average $10 million per attack, and industrial breaches reached $5.56 million in 2025. Add compliance fines and customer trust loss, and the true cost multiplies fast.
What to Do Next
After 12 years working with IoT applications across industries, here’s what I’d tell anyone getting started or going deeper:
First: don’t chase the technology. Chase the problem. The best IoT deployments start with a specific pain point (spoiled inventory, unpredictable machine failures, wasted energy) and work backward to find the right sensors, connectivity, and platform.
Second: treat security as a first-class requirement, not an afterthought. With 84% of IoT adopters reporting breaches, this isn’t optional. Budget for it. Staff for it. Train for it.
Third: invest in people. The technology is only as good as the team managing it. IoT training that covers the full stack, from hardware to cloud to security, will give you a competitive edge that no vendor can sell you out of a box.
IoT applications are already transforming healthcare, manufacturing, agriculture, energy, and the way we live at home. The question isn’t whether to engage with this technology. It’s whether you’ll do it thoughtfully, securely, and with the right skills on your team.
Got a question about implementing IoT in your organization? Share your experience or challenge in the comments below, or explore our related guides on IoT security best practices and smart home setup.



Pingback: What Is VPN and How Does It Work? - Acroan.com
Pingback: The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Modern Accounting Management